STD Testing & Treatment
STDs are transmitted through sexual contact, and early detection is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of transmission.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that there are approximately 20 million new STD infections each year—almost half of them among young people ages 15 to 24. At Home of Grace Inc., we understand that discussing sexually transmitted diseases can be sensitive, and we’re here to provide you with compassionate care with confidential STD testing and treatment.
Our STD Services
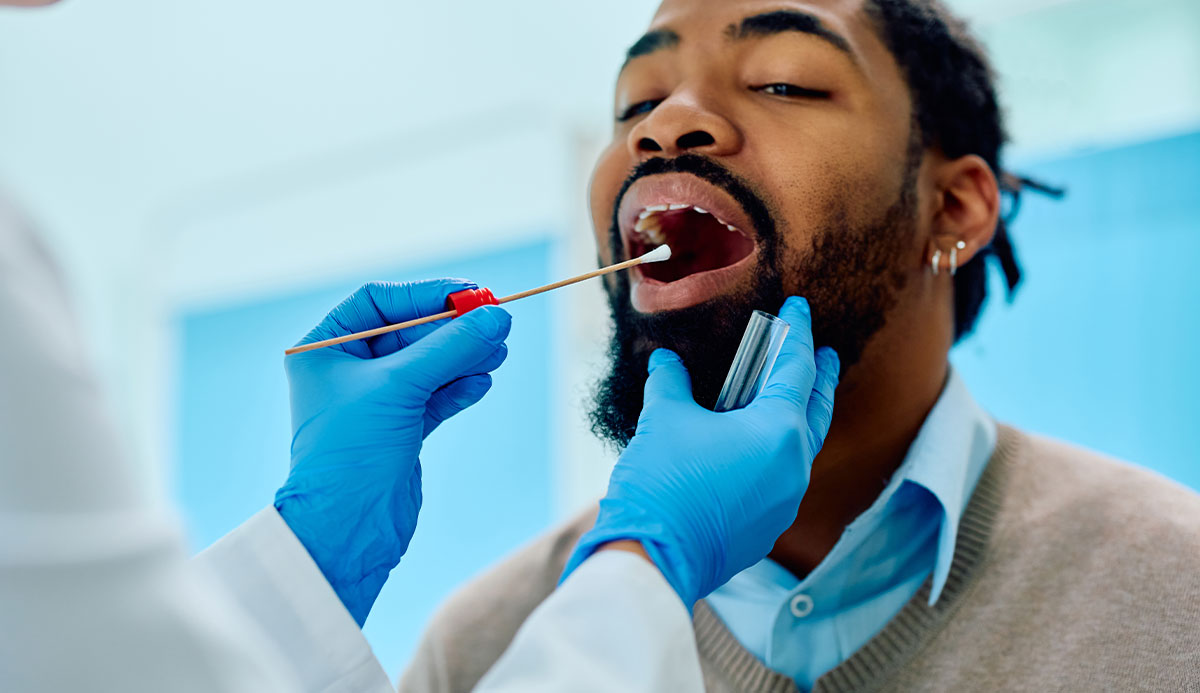
STD Testing
We offer complimentary and confidential testing for various STDs, including chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and more. Our rapid tests provide quick results, allowing you to take immediate steps toward better health.
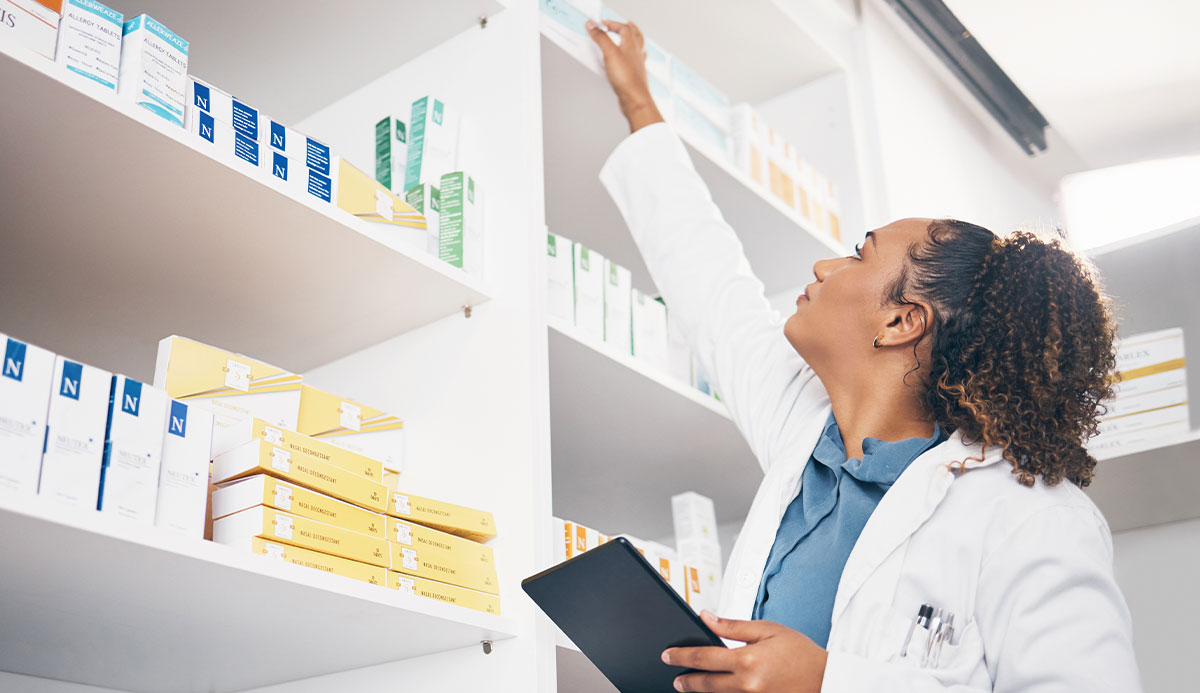

STD Treatment
If you test positive, our healthcare professionals will work with you to develop a customized antibiotic treatment plan tailored to your specific needs, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
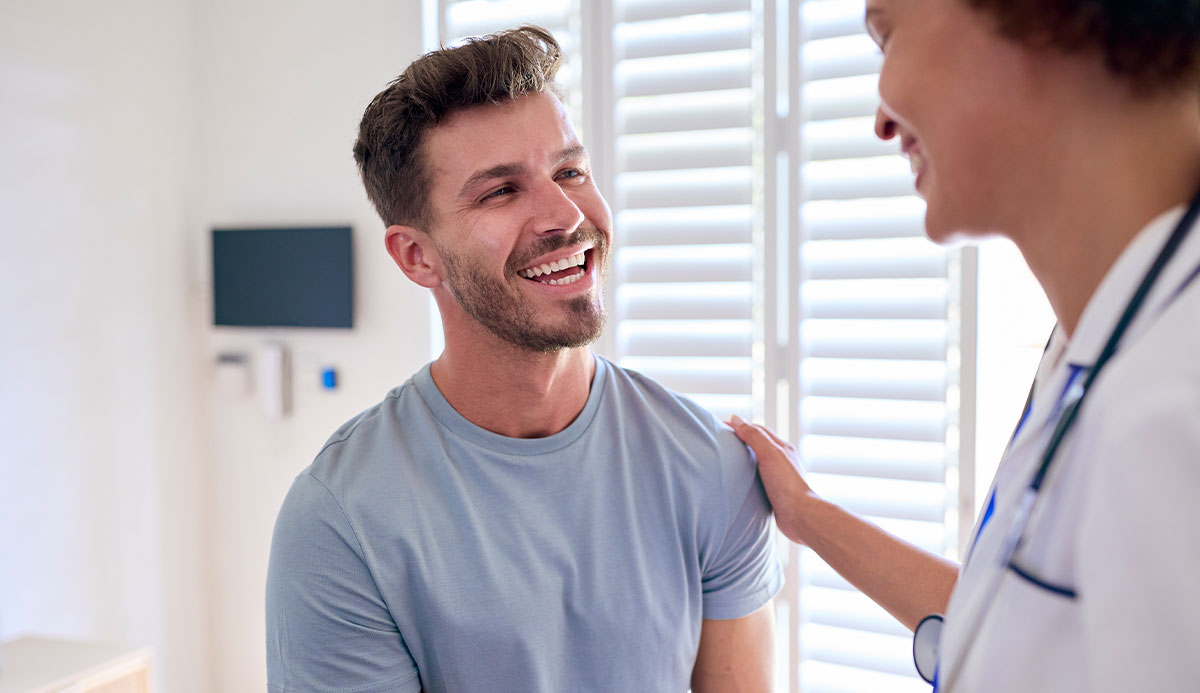

STD Management
We believe in empowering our patients with knowledge. Our team provides education on safe practices and prevention strategies to help you maintain your health and well-being.
Common Questions About STDs
What is an STD or an STI?
A sexually transmitted disease or a sexually transmitted infection, STD and STI, respectively, is what the name suggests: a disease or an infection that is transmitted through sexual intercourse. Most STDs can be contracted from any or all forms of unprotected sexual intercourse. However, sex is not the only route of transmission for this group of diseases.
What are the type of STDs?
There are almost 20 identified STDs that are known to infect humans caused by viruses, bacteria, and protozoa. All of these diseases are transmitted from sexual intercourse, among other routes. Although all of these STDs are common, some are more prevalent than others. HPV, Herpes, Syphilis, Chlamydia, HIV, and Gonorrhea are the most common types of STDs in the U.S. and also worldwide.
All STDs share a standard route of transmission, but they have different characteristics regarding patient presentation—genital herpes, Syphilis, and HPV present as genital warts. Hepatitis B and C present as an inflammation of the liver. HIV lowers the host’s immune response and manifests as the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS).
How does one get screened for STDs?
Numerous tests for detecting STDs are available. The types of tests used to diagnose STD depend on the particular disease. Testing also depends on your sexual history, your past medical history, and the symptoms you are presently having. STD testing is often painless, readily available in the United States, and free through Independent Medical Group!
How is STD testing carried out?
There are different tests to identify different STDs. The choice to apply a diagnostic test for an STD depends on the type of disease, your current symptoms, and your past medical history.
Usually, the process of diagnosing an STD, or any disease for that matter, has two phases. The first phase is the clinical history and examination. This is where your doctor will look for any signs and symptoms that might give him an idea about your disease. The doctor may ask you a series of questions about your sexual history, the method of protection used (if any), and the number of your active and past sexual partners. There might also be other questions depending on the type of disease.
The second phase is where your doctor takes some samples and sends them out for investigations. Depending on the type of infection, your doctor might take:
- Blood samples
- Urine samples
- Stool samples
- Swab samples from your mouth, genitalia, and blisters or open sores
The process of taking samples is painless. Usually, test results can be received in 5-7 days. Most hospitals and clinics have onboard testing facilities. Others send these samples out to labs, causing a slight delay with your test results.
Which approach is the best for testing for STDs?
STDs are extremely common in the United States as well as worldwide. STDs can also be present without any apparent physical symptoms. This absence of symptoms is the reason why STD testing is so important in order to contain their transmission.
What is the best STD testing method?
There are many ways to get tested for STDs. Depending on your symptoms your doctor might take blood, urine, or mucus samples to check for the presence of an infection. Specific tests are also available for certain STDs.
There are various tests for different sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). The kind of test a person gets will rely on the type of STD, signs and symptoms (like sores, discharge, or pain), as well as his or her medical and also sex-related history.
To get this history, a physician or nurse practitioner (NP) will certainly inquire about points like the amount of partners the individual has actually had. Afterwards, the physician or NP will certainly check out the person’s genital areas. For women that have symptoms of STDs, this could include a pelvic exam. Women who do not have signs and are simply obtaining screened for Sexually transmitted diseases as part of a regular checkup possibly won’t require a pelvic examination.
Based on what’s gained from the interview as well as exam, the physician or NP may take several of these samples:
- a blood sample (from either a blood draw or a finger prick)
- a urine sample
- a swab within the mouth
- a swab from the genitals, such as the urethra in people or the cervix in ladies
- a swab of any discharge or sores
Sometimes, the sample can be tested right there in the doctor’s office. Other times, the sample is sent to a lab and also the results come later on. It depends on the office and the sort of infection medical professionals are examining for.
STIs can be asymptomatic meaning there are no signs or symptoms to report. Commonly there are no indications that a person has one. That’s not always an advantage. These “covert” STDs can still put individuals in danger for health problems. Anyone who is sexually active should receive an STI screening regularly to know your status.
It is important to note however that STD testing is not part of the routine testing procedures. You might have to ask your IMG healthcare provider specifically for an STD test if you suspect you have such a disease. Most STDs can be diagnosed in a clinic. Others need specialized equipment in a dedicated lab setting.
What is the treatment of STDs ?
There are several treatments available for STDs. While most STDs that are caused by bacteria and other pathogens are curable, some are much more difficult to treat than others due to antibiotic-resistant strains. STDs caused by viruses are generally incurable and the person has to live with the disease for the rest of their life. However, there are treatments available that can suppress the symptoms enough to allow a relatively healthy lifestyle for patients with such diseases.
Medications to Treat STDs
STDs can be treated with antibiotics or antiviral drugs depending on the causative pathogen. There are also vaccines available that provide immunity to some STDs. In addition, several prophylaxis regimens exist that can help protect you from acquiring the disease in the first place.
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms of an STD, or if you have reason to believe that you were exposed to one, contact your doctor immediately. Early detection and prompt treatment can increase your chances of successful treatment. Additionally, always use safe sex practices to minimize your risk of acquiring an STD by minimizing exposure.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are extremely effective against STDs caused by bacteria and even parasites. Gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis are all examples of STDs that are usually cured by antibiotics. Generally, antibiotics often cure the infection they are effective against in a dosage varies.
Your doctor may prescribe you antibiotics according to international guidelines. Following the given prescription according to the schedule is extremely important for the elimination of the disease. If you have trouble following the schedule of a treatment regime, your doctor may advise a simpler alternative schedule for you to follow.
It is important to abstain from sexual intercourse at least seven days after you’ve completed your antibiotic course. This interval ensures complete eradication of the infection before it can be passed to another person through sex. Retesting is also an important factor to consider after the completion of your treatment. Retesting informs your doctor of your health status as well as the efficacy of the treatment employed.
Antivirals
STDs caused by viruses are harder to treat. They are also hard to completely cure as most viruses continue to live inside the host forever once an infection has taken place. However, there are several treatment options available to minimize the symptoms of the infection. Minimizing the symptoms ensures a relatively healthy state for the patient who has viral STDs.
HIV, HPV, Herpes, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C are some of the examples of STDs caused by viruses. All of these are incurable but there are effective treatment regimes available against them. Antiviral therapy is available against Hepatitis B and Herpes. This treatment is very effective in lowering the viral load in a patient and allowing daily activities to continue. Antiretroviral therapy works well against HIV. Additionally, your doctor may prescribe creams, or even minor surgeries, to counter genital warts and sores, cold sores, and other such complications caused by these diseases.
Vaccines and Prophylaxis Medication
Vaccination against a disease prevents the disease process from ever initiating in a person. HPV, Hepatitis A, and Hepatitis B have an effective vaccine that works well to protect from these conditions. There is no vaccine for other STDs, such as those caused by bacteria and parasites, at the moment.
Prophylaxis medication helps prevent the onset of infection after a possible exposure. PrEP, or Pre Exposure Prophylaxis, for HIV is a medication regime that prevents infection when taken daily before a possible exposure to HIV. Similarly, nPEP – or Post Exposure Prophylaxis – is another medication regime that prevents HIV infection after a possible exposure to the virus if initiated within 3 days of HIV exposure.
Which antibiotics are used for the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases?
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) or Sexually Transmitted Infections (STDs), caused by bacteria, such as syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia, are generally easier to treat and are often curable when treated with the right antibiotics. Those caused by viruses, though manageable, are often not curable. These include Herpes and HIV/AIDS and are treated using antiviral drugs instead of antibiotics.
When and how are antibiotics administered?
Antibiotic therapy is a mainstay in treating sexually transmitted diseases. Depending on the type of infection your healthcare provider may decide what antibiotics are required. These may then be administered through various means of treatment.
- A single injection,
- A course of pills taken over a few days
- And as a cream/ointment locally applied to the infected area.
Should you get tested?
If you answer yes to any of the the questions below, then it’s time to get tested to keep both you and others safe.
- RAre you uncertain your STD status?
- RHave you had unprotected sex within the last 12 months?
- RHave you had oral sex but you have not been tested?
- RHave you shared needles or reused dirty needles within the last 12 months?
Remember, taking care of your sexual health is a vital part of your overall well-being, and we’re here to support you every step of the way. We recommend everyone who is sexually active under the age of 25 to get tested for STDs annually.
Ready to Get Tested?
We’re here to provide compassionate, comprehensive care tailored to your needs. Reach out to us today at (386) 279-7002 to learn more about our services or to schedule an appointment.
You’ve got more questions…
Let Us Help
Remember, your health is your power—and we’re here to help you protect it. Visit us today and take the first step toward a healthier, brighter future.